We know how to prevent and treat colon cancer. But last year, colon cancer still killed more than 56,000 men and women. Many of them do not have to die. It can prevent and cure 90% of colon cancers. A simple test called a colonoscopy can detect and eliminate the cause of colon cancer.
1. Use Colonoscopy to Prevent and Treat Cancer
We know how to prevent and treat colon cancer through this simple, almost painless method called colonoscopy. Hopefully it is made to understand that Colonoscopy is one of the gold standard for detecting colon cancer. This is a valuable screening tool.The actual process takes less than twenty minutes. You are calm and may fall asleep during the exam. A gastroenterologist or surgeon inserts an elongated flexible tube called a colonoscope into the rectum and guides it into the colon. A sophisticated miniature camera helps to find tissue blocks called polyps. If one or more suspicious polyps are found, they will be removed and biopsied during the examination. Most polyps can be removed by wire loops, and small polyps can be destroyed by electrical contact. Air can be introduced to extend the view of the colon. In most cases, early colon cancer can be prevented and cured by removing colon polyps.
The operation is usually painless and there are no complications. The risk of bleeding after removal of larger polyps is lower. However, removal of very large polyps may require surgery.
2. What is Colon Cancer?
The colon consists of the upper 4 to 5 feet of the large intestine, and the rectum consists of the lower 6 inches. Colon cancer is colorectal cancer, the lower part of the digestive system, called colorectal cancer, also called colon cancer. A closely related rectal cancer is cancer of the last 6 inches of the colon. Together, they are often called colorectal cancer. According to the American Cancer Society, about 112,000 people are diagnosed with colon cancer every year, and about 41,000 new cases of rectal cancer are diagnosed every year.3. Causes of Colon Cancer
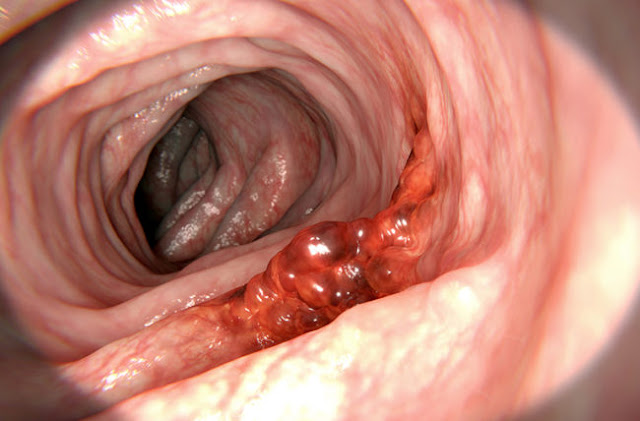
Colon cancerMost cases of colon cancer start in small, cancer-free (benign) cell clusters called adenomatous polyps. Colon polyps are abnormal mushroom-shaped growths that line the large intestine and extend into the intestinal tube. Over time, some of these polyps will become colon cancer. Colon polyps occur in 15% to 20% of adults. The likelihood of polyps becoming cancerous depends on many factors.
Normally, cancer occurs when healthy cells change, divide and lose control. Over a long period of time, certain areas of abnormal cells may become cancerous. Like most cancers, the exact cause of colon cancer is unclear. As the disease progresses, colon cancer can penetrate the colon wall and spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Colon polyps are usually small and have almost no symptoms. Defiantly, regular screening test is the most vital test that can help prevent colon cancer by identifying polyps before they become cancerous. During colonoscopy, colon polyps are removed. If colon polyps are not removed, the risk of cancer will increase over time. It is made to understand that after 20 years, the risk of cancer moves up to 24%. However, after removing polyps, the risk of colon cancer is only 2.3%.
4. Symptoms of Colon Cancer
Most polyps have no symptoms and are usually found accidentally during surgery. Many patients with colon cancer have no symptoms in the early stages of the disease. When symptoms appear, they may be different, depending on the size of the cancer and its location in the large intestine. These symptoms are not unique to colon cancer. They may indicate other conditions, but inspections are always recommended.- Diarrhea or constipation or changes in stool consistency
- Rectal bleeding or blood in the stool
- Cramps, gas or pain are part of Persistent abdominal discomfort
- Abdominal pain during defecation
- The stomach is not completely empty
- Weakness or fatigue
- Unexplained weight loss
5. Prepare the Colonoscopy Procedure
ColonoscopyTell your doctor about any medical conditions and any types of medications you are taking. You will also need to obtain a bowel preparation kit from the pharmacy, which includes laxatives and instructions. Colonoscopy requires that the intestinal cavity is empty so that the lining of the colon can be seen. You will receive instructions on diet and laxatives the day before the operation. You will maintain a clear liquid diet of fat-free broth, broth, water, gelatin, black coffee and pure tea. The bowel preparation kit includes liquid laxatives and stool softeners. Since the laxative tastes unpleasant, it is recommended that you refrigerate it and drink it with a straw. You should not eat or drink for four to six hours before the test.
6. Expectations During Colonoscopy
The actual colonoscopy procedure usually takes less than 20 minutes. You will get intravenous fluids and medicines to help you relax. Most patients fell asleep and knew nothing about the examination itself. After the colonoscopy, you will rest for an hour until the medicine runs out. You will not be fully alert and warned not to drive during the rest of the day. There is usually no discomfort, but cramps can be relieved by pumping or walking. Test results can be obtained after a few days of the procedure. If you experience persistent pain, bleeding or fever, please contact your healthcare provider.7. Prevent Colon Cancer by Reducing risk Factors
Reducing risk factors can also prevent colon cancer. These factors increase your risk of colon cancer:- You are over 50 years old.
- You already have colon cancer or colorectal polyps.
- You have inflammatory bowel disease, such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease.
- You have certain inherited genetic diseases, or a family history of colon cancer and colon polyps.
- You smoke, drink or lead an unhealthy lifestyle.
- Your lifestyle is sedentary.
- You are obese or have diabetes.
- If dietary fiber is low and fat and calories are high, diet may be a factor. The eating habits of Western countries are a risk factor.
- You drink too much.
- You have a growth hormone disease.
- You have received abdominal radiation therapy to treat cancer.